


CYTOGENETIC ABNORMALITIES IN ACUTE LEUKEMIA
PATIENTS: RESULTS OF CONVENTIONAL CYTOGENETICS
AND FLUORESCENT IN SITU HYBRIDIZATION ANALYSES
Yilmaz Z1,*, Sahin FI1, Kizilkilic E2, Karakus S3, ?zbek N4, Boga C2, ?zdogu H2
*Corresponding Author: Zerrin Yilmaz, MD, Baskent University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Medical Biology and Genetics, Kubilay Sokak No. 36, 06570 Maltepe, Ankara, Turkey; Tel.: +90-312-232-44-00/139; Fax: +90-312-232-39-12; E-mail: zerriny@baskent.edu.tr
page: 33
|
|
RESULTS
A total of 71 patients, aged between 9 months and 72 years, were included in the study. Of the 41 AML cases, 25 were female, 16 were male. Only one patient was a pediatric AML case. Thirty patients were diagnosed as ALL, of whom 10 were female and 20 were male. Seven of the ALL patients were pediatric cases. In 28 patients, chromosome rearrangements were detected either by conventional cytogenetics or by FISH. The findings in these patients are shown in Tables 2 and 3.
The AML Patients. Nine patients were initially diagnosed as AML-M3. Two patients had hypodiploidy with between 38 and 43 chromosomes of which one= revealed t(15;17) and the other t(9;22) after hybridization. One patient had trisomy 8, another had trisomy 2 and another had a marker chromosome in their karyotypes. An AML-M2 patient had a 46,XY,t(8;21) (q22;q22) karyotype. One patient had a complex karyotype designated as 45,XY, 5q-,5p-,-7,11q23-,16q+, and revealed an MLL deletion after hybridization with the MLL probe. In three AML patients, we could not obtain good quality metaphases. The remaining patients revealed normal karyotypes by conventional G-banding studies.
We detected t(9;22) after hybridization in five patients who had normal karyotypes by conventional analyses. One patient who had the t(9;22) translocation, also had a trisomy 22 clone detected by hybridization.
All but two AML patients were also hybridized with the inv(16) probe and had normal signals. The patient with a marker chromosome in her karyotype, had inversion 16 and a male patient with a normal karyotype also had inversion 16 (Table 2).
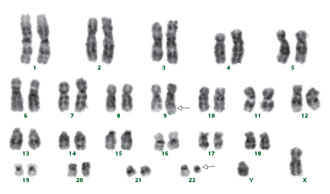
Figure 1. The G-banded karyotype of patient 25 with t(9;22). Partner chromosomes are indicated by arrows.
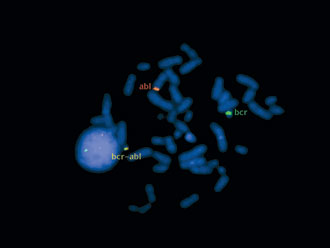
Figure 2. The metaphase spread of patient 25, hybridized with the BCR-ABL translocation probe, is shown. The translocation region is shown by the yellow annotation.
The ALL Patients. Of the 30 ALL patients included in this study, one had a 46, XX,der(22)t(15p;22q) clone in 50% of her metaphases. Two patients had t(9;22) by conventional G-banding in their karyotypes (Fig. 1), which was also seen after hybridization with the t(9;22) probe (Fig. 2). We did not observe good quality metaphases in one patient, in whom a t(9;22) translocation was detected by FISH. The rest of the ALL patients had normal karyotypes. All patients were hybridized separately with the t(9;22), t(15;17), and MLL probes. Two patients with normal karyotypes had t(9;22). There was also one rearrangement with the MLL probe in a pediatric ALL patient.
Table 2. Leukemia type, karyotype abnormalities and FISH analysis results in patients in whom an abnormal clone was detected either by cytogenetics or by FISH
Patient |
Leukemia Type |
Cytogenetic Findings |
t(9;22) |
t(15;17) |
inv(16) |
MLL |
1 |
AML-M3 |
46,XY |
[+] trisomy 22 |
[+] |
[–] |
[–] |
2 |
AML-M3 |
46,XY |
[–] |
[+] |
[–] |
[–] |
3 |
AML-M3 |
46,XY |
[–] |
[+] |
[–] |
[–] |
4 |
AML |
47,XX,+2[18]/46,XX[2] |
[–] |
[–] |
[–] |
[–] |
5 |
AML-M2 |
46,X7,t(8;21)(q22;q22) |
[–] |
[–] |
[–] |
[–] |
6 |
AML-M1 |
46,XX |
[+] |
[–] |
[–] |
[–] |
7 |
AML |
47,X7,+8[14]/46,XY |
[–] |
[–] |
[–] |
[–] |
8 |
AML |
46,XX |
[+] |
[–] |
[–] |
[–] |
9 |
AML |
47,XY,+2[10]/46,X7[10] |
[–] |
[–] |
[–] |
[–] |
10 |
AML-M3 |
46,XX |
[–] |
[+] |
[–] |
[–] |
11 |
AML-M4 |
47,XX,+mar[5]/46,XX[15] |
[–] |
[–] |
[+] |
[–] |
12 |
AML |
Hypodiploidy |
[–] |
[–] |
[–] |
[–] |
13 |
AML |
46,XY |
[–] |
[–] |
[+] |
[–] |
14 |
AML-M3 |
46,XX |
[–] |
[+] |
[–] |
[–] |
15 |
AML-M3 |
46.XX |
[–] |
[+] |
[–] |
[–] |
16 |
AML |
Not available |
[+] |
[–] |
[–] |
[–] |
17 |
AML |
Hypodiploidy |
[+] |
[–] |
[–] |
[–] |
18 |
AML-M3 |
46,XX |
[–] |
[+] |
[–] |
[–] |
19 |
AML |
45,XY,5q-,5p-,-7,11q23-, 16q+ |
[–] |
[–] |
[–] |
[+] |
20 |
AML-M3 |
46,XX |
[–] |
[+] |
[–] |
[–] |
21 |
AML-M3 |
46,XX |
[–] |
[+] |
[–] |
[–] |
22 |
ALL |
46,XX,der(22)t(15p;22q) |
[–] |
[–] |
NHa |
[–] |
23 |
ALL |
Not available |
[+] |
[–] |
NHa |
[–] |
24 |
ALL |
46,XY,der22t(9;22)[5]/46,XY[15] |
[+] |
[–] |
NHa |
[–] |
25 |
ALL |
46,XY,der22t(9;22)[2]/46,XY[18] |
[+] |
[–] |
NHa |
[–] |
26 |
ALL |
46,XY |
[+] |
[–] |
NHa |
[–] |
27 |
ALL |
46,XY |
[+] |
[–] |
NHa |
[–] |
28 |
ALL |
46,XX |
[–] |
[–] |
NHa |
[+] |
Table 3. Results of conventional cytogenetics or FISH abnormalities in the patients.
Leukemia Type |
AML |
ALL |
Number of Patients |
41 |
30 |
Conventional Cytogenetics (%) |
19.5 |
10.0 |
FISH (%) |
31.7 |
13.3 |
|
|
|
|



 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (2), 2024 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (1), 2024 |
Number 26
Number 26 VOL. 26(2), 2023 All in one |
Number 26
VOL. 26(2), 2023 |
Number 26
VOL. 26, 2023 Supplement |
Number 26
VOL. 26(1), 2023 |
Number 25
VOL. 25(2), 2022 |
Number 25
VOL. 25 (1), 2022 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(2), 2021 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(1), 2021 |
Number 23
VOL. 23(2), 2020 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(2), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(1), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22, 2019 Supplement |
Number 21
VOL. 21(2), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21 (1), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21, 2018 Supplement |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (2), 2017 |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (1), 2017 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (2), 2016 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (1), 2016 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (2), 2015 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (1), 2015 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (2), 2014 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (1), 2014 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (2), 2013 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (1), 2013 |
Number 15
VOL. 15 (2), 2012 |
Number 15
VOL. 15, 2012 Supplement |
Number 15
Vol. 15 (1), 2012 |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (2), 2011 |
Number 14
The 9th Balkan Congress of Medical Genetics |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (1), 2011 |
Number 13
Vol. 13 (2), 2010 |
Number 13
Vol.13 (1), 2010 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (2), 2009 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (1), 2009 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (2),2008 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (1),2008 |
Number 10
Vol.10 (2), 2007 |
Number 10
10 (1),2007 |
Number 9
1&2, 2006 |
Number 9
3&4, 2006 |
Number 8
1&2, 2005 |
Number 8
3&4, 2004 |
Number 7
1&2, 2004 |
Number 6
3&4, 2003 |
Number 6
1&2, 2003 |
Number 5
3&4, 2002 |
Number 5
1&2, 2002 |
Number 4
Vol.3 (4), 2000 |
Number 4
Vol.2 (4), 1999 |
Number 4
Vol.1 (4), 1998 |
Number 4
3&4, 2001 |
Number 4
1&2, 2001 |
Number 3
Vol.3 (3), 2000 |
Number 3
Vol.2 (3), 1999 |
Number 3
Vol.1 (3), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.3(2), 2000 |
Number 2
Vol.1 (2), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.2 (2), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.3 (1), 2000 |
Number 1
Vol.2 (1), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.1 (1), 1998 |
|
|

