


CHROMOSOME ABNORMALITIES IN SPONTANEOUS
ABORTIONS: APPLICATION OF MULTICOLOR
FLUORESCENT IN SITU HYBRIDIZATION AND
ORIGINAL DNA PROBES FOR CHROMOSOMES
1, 9, 13, 14, 16, 18, 21, 22, X AND Y
Vorsanova SG1,*, Kirilova EA2, Yurov YB3, Kolotii AD1,
Monakhov VV3, Iourov IY3, Beresheva AK1
*Corresponding Author: : Professor Dr. Svetlana G. Vorsanova, Director of Molecular-Cytogenetic Laboratory of Neuropsychiatric Diseases, Institute of Pediatrics and Children Surgery, Russian Ministry of Health, TaldomŽskaya str 2, 127 412 Moscow, Russia; Tel.: +7-095-484-1948; Fax: +7-095-952-8940; E-mail: y_yurov@ yahoo.com
page: 49
|
|
RESULTS
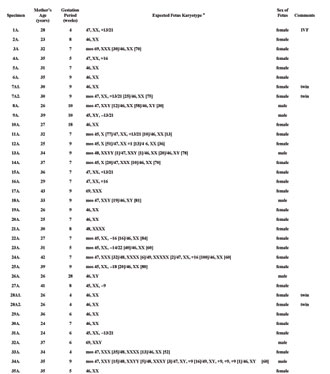
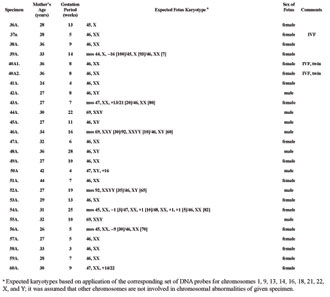
We applied two- or three-color FISH using DNA probes for chromosomes 1, 9, 13, 14, 16, 18, 21, 22, X, and Y, to investigate chromosomal abnormalities in 63 specimens of spontaneous abortions, including three twin pregnancies. The expected karyotypes, based on application of a probe set for the 10 chromosomes listed below, are presented in Table 1. We cannot exclude the presence of chromosomal aneuploidies involving other chromosomes (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 15, 17, 19, 20) not been tested by FISH in the present study.
The chromosomal abnormality was found in 39 (61.9%) spontaneous abortion specimens. The most common chromosomal abnormality was aneuploidy of chromosomes 13 or 21 (seven specimens) (17.9%), chromosome 16 (six specimens) (15.4%), and sex chromosomes (11 specimens) (28.2%). An abnormality of chromosome 1 was found in two specimens (5.1%), chromosome 9 in three specimens (7.7%), chromosome 14 or 22 in two specimens (5.1%), and chromosome 18 in one specimen (2.7%). Polyploidy (triploidy and tetraploidy) was found in seven specimens (17.9% from abnormal specimens) with an abnormal karyotype. The percentage of abnormal male fetuses was 73.3% (11/15 specimens) and abnormal female fetuses was 50% (24/48 specimens). Two examples of results obtained by FISH are presented in Fig. 1. More than half (20/39 or 51.3%) of spontaneous abortions with chromosomal abnormalities had mosaic forms of aneuploidy or polyploidy. We have detected a prevalence of female fetuses (male/female ratio 15/48).
Table 1. Fluorescent in situ hybridization analysis of spontaneous abortions: application of an original DNA probe set for chromosomes 1, 9, 13, 14, 16, 18, 21, 22, X and Y (expected karyotypes based on application of corresponding set of DNA probes).
|
|
|
|



 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (2), 2024 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (1), 2024 |
Number 26
Number 26 VOL. 26(2), 2023 All in one |
Number 26
VOL. 26(2), 2023 |
Number 26
VOL. 26, 2023 Supplement |
Number 26
VOL. 26(1), 2023 |
Number 25
VOL. 25(2), 2022 |
Number 25
VOL. 25 (1), 2022 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(2), 2021 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(1), 2021 |
Number 23
VOL. 23(2), 2020 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(2), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(1), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22, 2019 Supplement |
Number 21
VOL. 21(2), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21 (1), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21, 2018 Supplement |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (2), 2017 |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (1), 2017 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (2), 2016 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (1), 2016 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (2), 2015 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (1), 2015 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (2), 2014 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (1), 2014 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (2), 2013 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (1), 2013 |
Number 15
VOL. 15 (2), 2012 |
Number 15
VOL. 15, 2012 Supplement |
Number 15
Vol. 15 (1), 2012 |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (2), 2011 |
Number 14
The 9th Balkan Congress of Medical Genetics |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (1), 2011 |
Number 13
Vol. 13 (2), 2010 |
Number 13
Vol.13 (1), 2010 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (2), 2009 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (1), 2009 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (2),2008 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (1),2008 |
Number 10
Vol.10 (2), 2007 |
Number 10
10 (1),2007 |
Number 9
1&2, 2006 |
Number 9
3&4, 2006 |
Number 8
1&2, 2005 |
Number 8
3&4, 2004 |
Number 7
1&2, 2004 |
Number 6
3&4, 2003 |
Number 6
1&2, 2003 |
Number 5
3&4, 2002 |
Number 5
1&2, 2002 |
Number 4
Vol.3 (4), 2000 |
Number 4
Vol.2 (4), 1999 |
Number 4
Vol.1 (4), 1998 |
Number 4
3&4, 2001 |
Number 4
1&2, 2001 |
Number 3
Vol.3 (3), 2000 |
Number 3
Vol.2 (3), 1999 |
Number 3
Vol.1 (3), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.3(2), 2000 |
Number 2
Vol.1 (2), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.2 (2), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.3 (1), 2000 |
Number 1
Vol.2 (1), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.1 (1), 1998 |
|
|

