


PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS OF TRANSLOCATION 13;13
PATAU SYNDROME: CLINICAL FEATURES OF TWO CASES
Pazarbaþi A1,*, Demirhan O1, Süleymanova-Karahan D1,Taþtemir D1,
Tunç E1, Gümürdülü D2
*Corresponding Author: Ayfer Pazarbaþi, Ph.D., Department of Medical Biology and Genetics,
School of Medicine, Çukurova University, 01330 Balcali, Adana, Turkey; Tel.: +90-322-338-70-
68; Fax: +90-322-338-65-72; E-mail: payfer@cu.edu.tr
page: 69
|
|
RESULTS
We checked the features of our two cases against the common features of trisomy 13 reported by Rios et al. [2] as shown in Table 2. Case 1 was a pregnant woman, 27 years of age, who was referred to our laboratory because of a history of malformations detected by USG. The karyotype was 46,XX, rob t(13;13) and the baby girl lived for only 1 month after birth. The parentís karyotypes were normal. Autopsy Findings. The female fetus at 24 weeks of gestation weighted 300 g and measured 32 cm crown-heel, 23 cm head circumference. The most striking anomaly was a single eye in the mid-forehead (cyclopia), in the face, there was no nasal aperture. Holoprosencephaly, proboscis, microphthalmia and heart septal defects were present in the newborn.Case 2 was a pregnant women, 28 years of age, who was referred to our laboratory for prenatal diagnosis at 14 weeks gestational age due to the history of malformations detected by USG. Prenatal ultrasound scanning revealed cystic hygroma, hydrothorax and hyperechogenic kidneys. The karyotpe was 46,XY, rob(13;13) (Figure 1a and 1b). The mother was induced to give birth after karyotype analyses were completed. The parentís karyotypes were normal. The aborted fetus was the first pregnancy of this mother and was examined histopathologically. Autopsy Findings. The male fetus weighted 35.1 g and measured 13 cm crown-heel, 9 cm crown-rump, 8 cm head circumference and 1.1 cm foot length. There were cleft lip and cleft palate, and micrognathia of the face. There was postaxial polydactyly of the feet. There was also omphalocele. Histopathologically, the internal organs of the fetus were unremarkable.
Table 2. Common Features of Trisomy 13
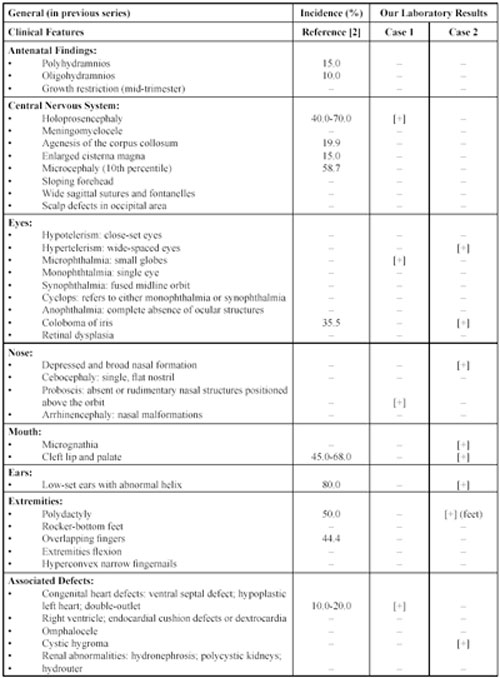
The following conditions were not found in either study: skin (capillary hemnagioma); tone (hypotonia/hypertonia); genitalia abnormalities (male: cryptorchidism, hypospadias, anomalous scrotum); (female: bicornuate uterus, duplicating system).
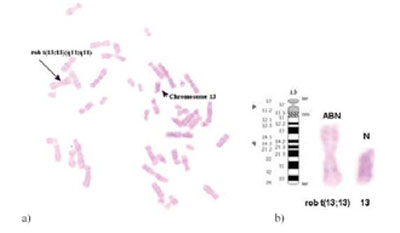
Figure 1. (a) Karyotype of the second case; (b) ideogram and G-banded images showing normal chromosome and translocation in chromosomes 13;13.
|
|
|
|



 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (2), 2024 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (1), 2024 |
Number 26
Number 26 VOL. 26(2), 2023 All in one |
Number 26
VOL. 26(2), 2023 |
Number 26
VOL. 26, 2023 Supplement |
Number 26
VOL. 26(1), 2023 |
Number 25
VOL. 25(2), 2022 |
Number 25
VOL. 25 (1), 2022 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(2), 2021 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(1), 2021 |
Number 23
VOL. 23(2), 2020 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(2), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(1), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22, 2019 Supplement |
Number 21
VOL. 21(2), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21 (1), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21, 2018 Supplement |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (2), 2017 |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (1), 2017 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (2), 2016 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (1), 2016 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (2), 2015 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (1), 2015 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (2), 2014 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (1), 2014 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (2), 2013 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (1), 2013 |
Number 15
VOL. 15 (2), 2012 |
Number 15
VOL. 15, 2012 Supplement |
Number 15
Vol. 15 (1), 2012 |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (2), 2011 |
Number 14
The 9th Balkan Congress of Medical Genetics |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (1), 2011 |
Number 13
Vol. 13 (2), 2010 |
Number 13
Vol.13 (1), 2010 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (2), 2009 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (1), 2009 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (2),2008 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (1),2008 |
Number 10
Vol.10 (2), 2007 |
Number 10
10 (1),2007 |
Number 9
1&2, 2006 |
Number 9
3&4, 2006 |
Number 8
1&2, 2005 |
Number 8
3&4, 2004 |
Number 7
1&2, 2004 |
Number 6
3&4, 2003 |
Number 6
1&2, 2003 |
Number 5
3&4, 2002 |
Number 5
1&2, 2002 |
Number 4
Vol.3 (4), 2000 |
Number 4
Vol.2 (4), 1999 |
Number 4
Vol.1 (4), 1998 |
Number 4
3&4, 2001 |
Number 4
1&2, 2001 |
Number 3
Vol.3 (3), 2000 |
Number 3
Vol.2 (3), 1999 |
Number 3
Vol.1 (3), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.3(2), 2000 |
Number 2
Vol.1 (2), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.2 (2), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.3 (1), 2000 |
Number 1
Vol.2 (1), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.1 (1), 1998 |
|
|

