


TRIPLOIDIES IN FIRST AND SECOND TRIMESTERS
OF PREGNANCIES IN TURKEY
Yilmaz Z1, Sahin FI1,*, Tarim E2, Kuscu E2
*Corresponding Author: Yilmaz Z1, Sahin FI1,*, Tarim E2, Kuscu E2*Corresponding Author: Professor Dr. Feride Iffet Sahin, Department of Medical Genetics,
Faculty of Medicine, Baskent University, Kubilay Sokak No: 36 Maltepe, 06570 Ankara, Turkey;
Tel.: +90-312-2324400/138; Fax: +90-312-2319134; E-mail: feridesahin@hotmail.com
page: 71
|
|
RESULTS
The clinical features of nine triploidy cases are shown in Table 1. Four of these were detected during cytogenetic analysis of amniotic fluid samples and five were detected during analysis of spontaneous abortions.
Among the 75 spontaneous abortion cases, we observed five triploidies and 11 other chromosome abnormalities consisting of seven autosomal trisomies (18, 21 and 22) and one sex chromosome trisomy (XXY) as numerical abnormalites, and two balanced and one unbalanced reciprocal translocation as structural abnormalities. The triploid abortions were between 9 and 13 weeks of gestation and maternal ages ranged between 24 and 45 years. Two cases had a history of a previous pregnancy loss (cases 1 and 2) which did not have any cytogenetic abnormalities. Cytogenetic analyses revealed a 69,XXY karyotype in four of the aborted fetuses and a 69,XXX karyotype in one. Except for case 5, all placenta samples from aborted fetuses were non molar, according to the pathological examination (Table 1).
Table 1. Clinical and laboratory findings for patients 1 through 9.
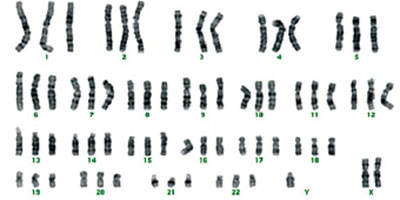
Figure 1. Karyotype obtained from amniotic fluid cell cultures of patient 9 has been reported as 69,XXY.
Of the 1,114 amniocentesis cases, 1,067 had increased risk for Down’s syndrome in second trimestertriple test screenings. No triploidies were detected in this group. Instead, we detected trisomy 21 in 10 cases, trisomy 18 in six cases, trisomy 13 in three cases, XXY in two cases, XXX in one case, monosomy X in two cases and balanced reciprocal translocation in four cases. The remaining 47 cases from the 1,114 amniocentesis cases had increased risk for trisomy 18 and four triploidy cases were detected in this group. These patients were aged between 19 and 35 years of age. Trisomy 18 risk at triple screening was 1/50 in cases 6 and 8, 1/10 in case 7 and 1/20 in case 9 (Table 1). Human chorionic gonadotropin values ranged between 0.16 and 0.23 multiples of median (MoM). Cytogenetic analyses revealed a 69,XXX karyotype in three cases and 69,XXY in one (Table1, Figure 1). All of these pregnancies were terminated and pathological examinations revealed non molar placentas. Minor fetal anomalies were seen during USG examination in these cases (Table 1, Figure 2).
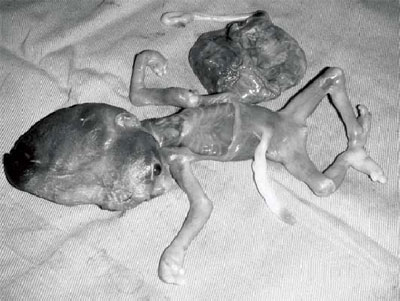
Figure 2. One of the fetuses with triploidy, after termination of pregnancy.
|
|
|
|



 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (2), 2024 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (1), 2024 |
Number 26
Number 26 VOL. 26(2), 2023 All in one |
Number 26
VOL. 26(2), 2023 |
Number 26
VOL. 26, 2023 Supplement |
Number 26
VOL. 26(1), 2023 |
Number 25
VOL. 25(2), 2022 |
Number 25
VOL. 25 (1), 2022 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(2), 2021 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(1), 2021 |
Number 23
VOL. 23(2), 2020 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(2), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(1), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22, 2019 Supplement |
Number 21
VOL. 21(2), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21 (1), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21, 2018 Supplement |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (2), 2017 |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (1), 2017 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (2), 2016 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (1), 2016 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (2), 2015 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (1), 2015 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (2), 2014 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (1), 2014 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (2), 2013 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (1), 2013 |
Number 15
VOL. 15 (2), 2012 |
Number 15
VOL. 15, 2012 Supplement |
Number 15
Vol. 15 (1), 2012 |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (2), 2011 |
Number 14
The 9th Balkan Congress of Medical Genetics |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (1), 2011 |
Number 13
Vol. 13 (2), 2010 |
Number 13
Vol.13 (1), 2010 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (2), 2009 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (1), 2009 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (2),2008 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (1),2008 |
Number 10
Vol.10 (2), 2007 |
Number 10
10 (1),2007 |
Number 9
1&2, 2006 |
Number 9
3&4, 2006 |
Number 8
1&2, 2005 |
Number 8
3&4, 2004 |
Number 7
1&2, 2004 |
Number 6
3&4, 2003 |
Number 6
1&2, 2003 |
Number 5
3&4, 2002 |
Number 5
1&2, 2002 |
Number 4
Vol.3 (4), 2000 |
Number 4
Vol.2 (4), 1999 |
Number 4
Vol.1 (4), 1998 |
Number 4
3&4, 2001 |
Number 4
1&2, 2001 |
Number 3
Vol.3 (3), 2000 |
Number 3
Vol.2 (3), 1999 |
Number 3
Vol.1 (3), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.3(2), 2000 |
Number 2
Vol.1 (2), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.2 (2), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.3 (1), 2000 |
Number 1
Vol.2 (1), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.1 (1), 1998 |
|
|

