


FLOURESCENT IN SITU HYBRIDIZATION AND
MOLECULAR ANALYSIS OF A SHORT GIRL WITH A
45,X/46,X, idic(X)(qter->p12.3::p12.3->qter) KARYOTYPE
Kitsiou S1,*, Mavrou A1, Kolialexi A1, Sofocleous C1,
Bakoula C2, Kanavakis E1, Dakou-Voutetakis C3
*Corresponding Author: Sofia Kitsiou, Associate Professor Medical Genetics, Athens University School of Medicine, “Aghia Sophia” Children’s Hospital, Thivon and Levadias Street, Athens 11 527, Greece; Tel.: +30-2107467463; Fax: +30-2107795553; E-mail: skitsiou@med.uoa.gr
page: 39
|
|
RESULTS
Cytogenetics. Among 100 metaphase spreads evaluated with G-banding from the proband, a mocaisism was revealed with a 45,X cell line (30%) and an euploid second cell line (70%) with one normal and one abnormal elongated X chromosome (Fig. 1). C-Banding showed that the abnormal idic (X) chromosome had two centromeres and seemed to consist of two Xs attached by their short arms, apparently close to the pseudoautosomal region (Xp21), with little, if any, material deleted as a result of the fusion. Chromosome analysis of both parents showed normal karyotypes.
Molecular Cytogenetic Analysis. The FISH analysis with X-chromosome paint stained one normal and the entire abnormal X chromosome. Dual color FISH showed one hybridization signal for each probe used on the normal X chromosome. On the abnormal idic (X) chromosome, two centromeres were displayed with DXZ1. No signals were present for the telomeres Xp/Yp and the SHOX gene. These findings indicate a complete deletion of the SHOX gene on the idic (X) and therefore, the karyotype of the proband is most probably of 45,X/46,X, idic(X)(qter-> p12.3: :p12.3->qter) (Figs. 2A and 2B).
Molecular Analysis . Molecular analysis of the family showed that the proband is heterozygous for the studied 4/8 dystrophin gene loci (Table 1). Family studies concerning the origin of the alleles provided little information for most of the examined loci.
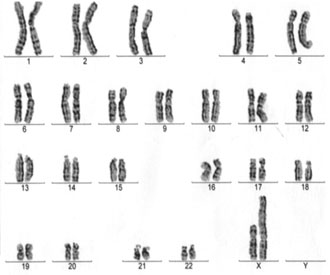
Figure 1. Karyotype of the proband showing the abnormal idic (X) chromosome.
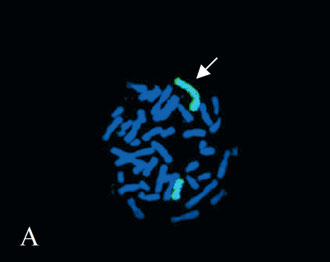
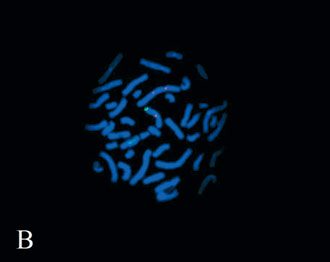
Figure 2. Fluorescent in situ hybridization analysis with A) whole X chromosome paint (the arrow points to the abnormal X chromosome), and B) DXZ1 (red signal) in combination with the SHOX gene probe (green signal).
|
|
|
|



 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (2), 2024 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (1), 2024 |
Number 26
Number 26 VOL. 26(2), 2023 All in one |
Number 26
VOL. 26(2), 2023 |
Number 26
VOL. 26, 2023 Supplement |
Number 26
VOL. 26(1), 2023 |
Number 25
VOL. 25(2), 2022 |
Number 25
VOL. 25 (1), 2022 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(2), 2021 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(1), 2021 |
Number 23
VOL. 23(2), 2020 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(2), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(1), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22, 2019 Supplement |
Number 21
VOL. 21(2), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21 (1), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21, 2018 Supplement |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (2), 2017 |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (1), 2017 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (2), 2016 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (1), 2016 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (2), 2015 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (1), 2015 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (2), 2014 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (1), 2014 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (2), 2013 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (1), 2013 |
Number 15
VOL. 15 (2), 2012 |
Number 15
VOL. 15, 2012 Supplement |
Number 15
Vol. 15 (1), 2012 |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (2), 2011 |
Number 14
The 9th Balkan Congress of Medical Genetics |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (1), 2011 |
Number 13
Vol. 13 (2), 2010 |
Number 13
Vol.13 (1), 2010 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (2), 2009 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (1), 2009 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (2),2008 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (1),2008 |
Number 10
Vol.10 (2), 2007 |
Number 10
10 (1),2007 |
Number 9
1&2, 2006 |
Number 9
3&4, 2006 |
Number 8
1&2, 2005 |
Number 8
3&4, 2004 |
Number 7
1&2, 2004 |
Number 6
3&4, 2003 |
Number 6
1&2, 2003 |
Number 5
3&4, 2002 |
Number 5
1&2, 2002 |
Number 4
Vol.3 (4), 2000 |
Number 4
Vol.2 (4), 1999 |
Number 4
Vol.1 (4), 1998 |
Number 4
3&4, 2001 |
Number 4
1&2, 2001 |
Number 3
Vol.3 (3), 2000 |
Number 3
Vol.2 (3), 1999 |
Number 3
Vol.1 (3), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.3(2), 2000 |
Number 2
Vol.1 (2), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.2 (2), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.3 (1), 2000 |
Number 1
Vol.2 (1), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.1 (1), 1998 |
|
|

