


DETECTION OF TRISOMY 21 BY QUANTITATIVE FLUORESCENCE POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION
Madalina Badila1*, Augustin Ofiteru1, Lorand Savu1, Dinu Florin Albu1,
Dragos T. Stefanescu2
*Corresponding Author: Badila Madalina
Genetic Lab SRL, Str. Garleni 3, Bl. C79, sector 6, 051651 Bucharest, Romania
Tel: +0421 4131423 ; Fax: +0421 4028091
E-mail: office@geneticlab.ro
page: 23
|
|
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
A total of 15 blood samples were investigated in this study by both conventional cytogenetic tehnique and QF-PCR method. Analysis of fluorescent amplified DNA samples is made qualitatively by determination of allelic signal number and quantitatively by measurement of allelic fluorescent intensity. Normal heterozygous samples display diallelic peaks corresponding to two different alleles with peak fluorescence intensity ratio of approximately 1:1, whereas normal homozygous samples display only one peak corresponding of two identical alleles (Fig. 1). Trisomic samples display either 3 peaks of similar intensity or 2 peaks but with fluorescence intensity ratio of approx. 2:1 [3].
All 5 normal individuals examined in our study was heterozygous and showed two allelic peaks for both D21S11 and Penta D STR markers with peak height ratio of 1:1. Four of ten 21 trisomic samples showed a triallelic pattern with peak height ratio of approximately 1:1:1 for both D21S11 and Penta D markers. Four trisomic samples showed a diallelic pattern with peak height ratio of 1.6 - 2.3 for D21S11 marker and 1.7 – 1.9 for Penta D marker. One trisomic sample displayed a triallelic pattern for D21S11 marker and a diallelic pattern with peak height ratio of 2.3 for Penta D marker whereas another trisomic sample showed a triallelic pattern for Penta D marker and a diallelic pattern with peak height ratio of 1.7 for D21S11 marker. Figure 2 (A) illustrates a trisomy 21 case with a triallelic pattern for both D21S11 and Penta D markers. Figure 2 (B) shows a trisomy 21 case with a diallelic pattern (2:1 dosage ratio) for both 21 chromosome markers.
The results obtained using quantitative fluorescent PCR were in concordance with the conventional cytogenetic results.
This study represent our first attempt to evaluate a molecular method for detection of trisomy 21. The preliminary data obtained successfully confirm the cytogenetic diagnosis of trisomy 21 and demonstrated that this tehnique is suitable for the rapid postnatal detection of Down syndrome.
(Badila)-.jpg)
Fig.1. Electroforetograms of amplification of a) a normal homozygous disomic sample; b) a normal heterozygous disomic sample; c) a triallelic trisomic sample; d) a diallelic trisomic sample (2:1 dosage ratio)
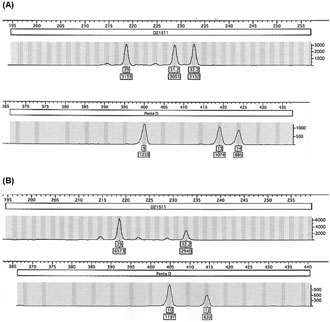
Fig.2. Electrophoretograms of fluorescent D21S11 and Penta D amplified STR markers. (A) a trisomy 21 affected patient with a triallelic pattern with peak height ratio of 1:1:1; (B) a trisomy 21 affected patient with a diallelic pattern with peak height ratio of 2:1
|
|
|
|



 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (2), 2024 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (1), 2024 |
Number 26
Number 26 VOL. 26(2), 2023 All in one |
Number 26
VOL. 26(2), 2023 |
Number 26
VOL. 26, 2023 Supplement |
Number 26
VOL. 26(1), 2023 |
Number 25
VOL. 25(2), 2022 |
Number 25
VOL. 25 (1), 2022 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(2), 2021 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(1), 2021 |
Number 23
VOL. 23(2), 2020 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(2), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(1), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22, 2019 Supplement |
Number 21
VOL. 21(2), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21 (1), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21, 2018 Supplement |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (2), 2017 |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (1), 2017 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (2), 2016 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (1), 2016 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (2), 2015 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (1), 2015 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (2), 2014 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (1), 2014 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (2), 2013 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (1), 2013 |
Number 15
VOL. 15 (2), 2012 |
Number 15
VOL. 15, 2012 Supplement |
Number 15
Vol. 15 (1), 2012 |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (2), 2011 |
Number 14
The 9th Balkan Congress of Medical Genetics |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (1), 2011 |
Number 13
Vol. 13 (2), 2010 |
Number 13
Vol.13 (1), 2010 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (2), 2009 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (1), 2009 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (2),2008 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (1),2008 |
Number 10
Vol.10 (2), 2007 |
Number 10
10 (1),2007 |
Number 9
1&2, 2006 |
Number 9
3&4, 2006 |
Number 8
1&2, 2005 |
Number 8
3&4, 2004 |
Number 7
1&2, 2004 |
Number 6
3&4, 2003 |
Number 6
1&2, 2003 |
Number 5
3&4, 2002 |
Number 5
1&2, 2002 |
Number 4
Vol.3 (4), 2000 |
Number 4
Vol.2 (4), 1999 |
Number 4
Vol.1 (4), 1998 |
Number 4
3&4, 2001 |
Number 4
1&2, 2001 |
Number 3
Vol.3 (3), 2000 |
Number 3
Vol.2 (3), 1999 |
Number 3
Vol.1 (3), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.3(2), 2000 |
Number 2
Vol.1 (2), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.2 (2), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.3 (1), 2000 |
Number 1
Vol.2 (1), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.1 (1), 1998 |
|
|

