


A NOVEL MUTATION OF THE ABCD1 GENE IN
SERBIAN X-ADRENOLEUKODYSTROPHY
Grkovic S1*, Nikolic R2, Djordjevic M1, Puzigaca Z2, Vujic D1, Ilic P2
*Corresponding Author: Dr. Sanja Grkovic, Department of Pediatrics, Mother and Child Health
Care Institute of Serbia, Ljeska 55, 11030 Belgrade, Serbia; Tel.:+38-1641548175; Fax: +38-113108276; E-mail: metlab@ sezampro.yu
page: 65
|
|
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Peroxisomal disorders are an extremely heterogeneous group of genetic disorders without strict correlation between clinical picture and biochemical abnormalities. The natural history of the disease course is known to be unpredictable. The analysis of VLCFAs in plasma is necessary as the first screening test for diagnosis of XALD. Sequence analysis (Figure 1) of the ABCD1 mutant allele in the proband revealed a novel point mutation 1519 (G>A) in exon 6, causing the change of glycine at position 507 into serine (G507S). So far, no established correlation between genotype and phenotype has been reported (4). The range of phenotypic expression in XALD and the prognosis for an affected male are unpredictably variable and cannot be predicted through levels of VLCFA in plas ma or cultured skin fibroblasts, the residual VLCFA β-oxidation activity present in XALD skin fibroblasts, the family history or the nature of the mutation identified in the ABCD1 gene of the patient (5). The same mutation can be associated with each of the known clinical phenotypes. The affected boy had developed neurological symptoms and Addison’s disease at 6 years old and a bone marrow transplant at age of 8 without any effect. This mutation in exon 6 caused the changes in the intracellular domain of ALDP and may lead to instability or loss of function of ALDP resulting in accumulation of VLCFAs. Further investigation of ALDP stability in this patient is needed to clarify the impact of this ABCD1 mutation. The childhood cerebral form of XALD is a severe metabolic disease without a definite effective therapy. Mutations in the ABCD1 gene have been identified in the majority of XALD patients, and almost 60% of mutations are non recurrent. In conclusion, analyses of mutations in patients with XALD is necessary, especially for carrier diagnosis and genetic counseling, since more than 900 different mutations in the gene have been reported.
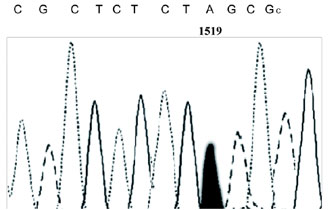
Figure 1. Partial sequence determination of the 1519 (G>A) point mutation of the ABCD1 gene for the hemizy gous proband.
|
|
|
|



 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (2), 2024 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (1), 2024 |
Number 26
Number 26 VOL. 26(2), 2023 All in one |
Number 26
VOL. 26(2), 2023 |
Number 26
VOL. 26, 2023 Supplement |
Number 26
VOL. 26(1), 2023 |
Number 25
VOL. 25(2), 2022 |
Number 25
VOL. 25 (1), 2022 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(2), 2021 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(1), 2021 |
Number 23
VOL. 23(2), 2020 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(2), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(1), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22, 2019 Supplement |
Number 21
VOL. 21(2), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21 (1), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21, 2018 Supplement |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (2), 2017 |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (1), 2017 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (2), 2016 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (1), 2016 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (2), 2015 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (1), 2015 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (2), 2014 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (1), 2014 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (2), 2013 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (1), 2013 |
Number 15
VOL. 15 (2), 2012 |
Number 15
VOL. 15, 2012 Supplement |
Number 15
Vol. 15 (1), 2012 |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (2), 2011 |
Number 14
The 9th Balkan Congress of Medical Genetics |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (1), 2011 |
Number 13
Vol. 13 (2), 2010 |
Number 13
Vol.13 (1), 2010 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (2), 2009 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (1), 2009 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (2),2008 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (1),2008 |
Number 10
Vol.10 (2), 2007 |
Number 10
10 (1),2007 |
Number 9
1&2, 2006 |
Number 9
3&4, 2006 |
Number 8
1&2, 2005 |
Number 8
3&4, 2004 |
Number 7
1&2, 2004 |
Number 6
3&4, 2003 |
Number 6
1&2, 2003 |
Number 5
3&4, 2002 |
Number 5
1&2, 2002 |
Number 4
Vol.3 (4), 2000 |
Number 4
Vol.2 (4), 1999 |
Number 4
Vol.1 (4), 1998 |
Number 4
3&4, 2001 |
Number 4
1&2, 2001 |
Number 3
Vol.3 (3), 2000 |
Number 3
Vol.2 (3), 1999 |
Number 3
Vol.1 (3), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.3(2), 2000 |
Number 2
Vol.1 (2), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.2 (2), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.3 (1), 2000 |
Number 1
Vol.2 (1), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.1 (1), 1998 |
|
|

