


MOLECULAR ANALYSIS OF FRIEDREICH’S ATAXIA
IN MACEDONIAN PATIENTS
Kocheva S1,2, Trivodalieva S1, Vlaski-Jekic S3, Kuturec M2, Efremov GD1,*
*Corresponding Author: Professor Dr. Georgi D. Efremov, Macedonian Academy of Sciences
and Arts, Research Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, Aven Krste Misirkov 2,
POB 428, 1000 Skopje, Republic of Macedonia; Tel: +3892-120253; Fax: +3892-115434; E-mail:gde@manu.edu
page: 61
|
|
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Representative electrophoregrams of PCR fragments from the amplification of GAA repeats in intron 1 of the frataxin gene in patients with FRDA and in healthy individuals are shown in Figure 1A and 1B, respectively. Polymerase chain reaction analyses of heterozygotes for expanded GAA alleles are shown in Figure 2. Of the 15 patients diagnosed with spinal cerebellar ataxia before 25 years of age, 14 (93.3%) were homozygous for the GAA expansion and all had two expanded alleles of same size and no detectable somatic instability. Only one patient with early onset of spinal cerebellar atax ia had two normal alleles, and this result excluded the diagnosis of FRDA. The 25 patients with late onset spinal cerebellar ataxia had two alleles in the normal size range (5-50 GAA repeats). Ten of these were heterozygotes and 15 were homozygous for normal alleles which excluded the diagnosis of FRDA.Molecular analysis of intron 1 of the frataxin gene in healthy individuals showed a range of GAA repeats from 5 to 50. Our results are concordant with already published data [1-4]. This long-range PCR protocol can be used as a diagnostic tool for FRDA and carrier detection.
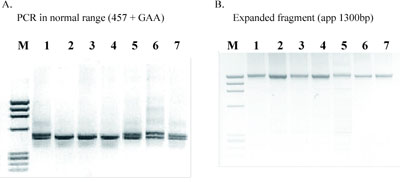
Figure 1. Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR products of intron 1 of the frataxin gene in healthy individuals (lanes 1-7) with different numbers of GAA repeats (A), and of seven patients with FRDA (lanes 1-7) (B); M: molecular weight marker.
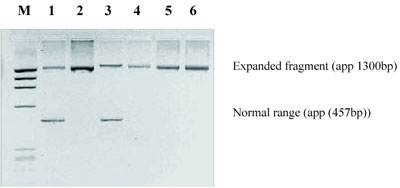
Figure 2. Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR products of patients (lanes 2, 5 and 6) and members of families with FRDA (lanes 1 and 3), showing the normal and expanded fragment (lanes 1 and 3); M: molecular weight marker.
|
|
|
|



 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (2), 2024 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (1), 2024 |
Number 26
Number 26 VOL. 26(2), 2023 All in one |
Number 26
VOL. 26(2), 2023 |
Number 26
VOL. 26, 2023 Supplement |
Number 26
VOL. 26(1), 2023 |
Number 25
VOL. 25(2), 2022 |
Number 25
VOL. 25 (1), 2022 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(2), 2021 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(1), 2021 |
Number 23
VOL. 23(2), 2020 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(2), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(1), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22, 2019 Supplement |
Number 21
VOL. 21(2), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21 (1), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21, 2018 Supplement |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (2), 2017 |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (1), 2017 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (2), 2016 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (1), 2016 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (2), 2015 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (1), 2015 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (2), 2014 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (1), 2014 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (2), 2013 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (1), 2013 |
Number 15
VOL. 15 (2), 2012 |
Number 15
VOL. 15, 2012 Supplement |
Number 15
Vol. 15 (1), 2012 |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (2), 2011 |
Number 14
The 9th Balkan Congress of Medical Genetics |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (1), 2011 |
Number 13
Vol. 13 (2), 2010 |
Number 13
Vol.13 (1), 2010 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (2), 2009 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (1), 2009 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (2),2008 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (1),2008 |
Number 10
Vol.10 (2), 2007 |
Number 10
10 (1),2007 |
Number 9
1&2, 2006 |
Number 9
3&4, 2006 |
Number 8
1&2, 2005 |
Number 8
3&4, 2004 |
Number 7
1&2, 2004 |
Number 6
3&4, 2003 |
Number 6
1&2, 2003 |
Number 5
3&4, 2002 |
Number 5
1&2, 2002 |
Number 4
Vol.3 (4), 2000 |
Number 4
Vol.2 (4), 1999 |
Number 4
Vol.1 (4), 1998 |
Number 4
3&4, 2001 |
Number 4
1&2, 2001 |
Number 3
Vol.3 (3), 2000 |
Number 3
Vol.2 (3), 1999 |
Number 3
Vol.1 (3), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.3(2), 2000 |
Number 2
Vol.1 (2), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.2 (2), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.3 (1), 2000 |
Number 1
Vol.2 (1), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.1 (1), 1998 |
|
|

