


ALLELE FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTIONS AT TWO
VNTR LOCI (APOB AND D1S80) AND TWO STR LOCI
(HUMTH01 AND HUMVWA) IN A SERBIAN POPULATION
SAMPLE, AND THEIR EVALUATION FOR PATERNITY
AND FORENSIC USE
Zarovni N, Georgijevic D, Grego E
*Corresponding Author: Dr. Edita Grego, Institute of Molecular Genetics and Genetic Engineering, Vojvode Stepe 444a, P.O. Box 446, 11001 Belgrade, Yugoslavia; Tel: +381 11 3976658; Fax: +381 11 3975808; E-mail: qwert@eunet.yu
page: 19
|
|
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
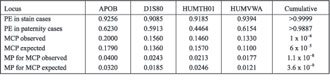
Allele frequencies determined by analysis of four polymorphic loci: APOB, D1S80, HUMTH01 and HUMVWA, in a restricted sample of 128 individuals from Serbia, are summarized in Table 1. Our results are in concordance with the data previously reported for various European populations [15-19].
To evaluate whether our population was in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, the c2 test was conducted based on comparison of observed and expected numbers of distinct genotypes (Table 2). An alternative exact test procedure [20] was also performed (data not shown). Both tests failed to detect any significant deviation from the equilibrium. In addition, no significant deviation in heterozygosity when compared to other populations was observed [21-24].
Two standard parameters were used to describe the forensic usefulness of the systems analyzed in this study: power of exclusion (PE) and match probability (MP) (Table 3). The combined value of PE for all tested loci, based on expected genotype frequencies, was over 0.99 in stain cases, while combined PE in paternity cases was 0.98. As a more conservative parameter, but a potentially very informative estimator of forensic usefulness, the frequency of the most common phenotype and its corresponding MP value, were calculated (see Table 3).
Based on the results of our study, there is no significant substructuring within the Serbian population. It is apparent that the tested systems are all polymorphic and potentially useful for forensic, paternity and medical application.
Table 1. Allele frequencies of APOB, D1S80, HUMTH01 and HUMVWA in a Serbian population (n = 128)
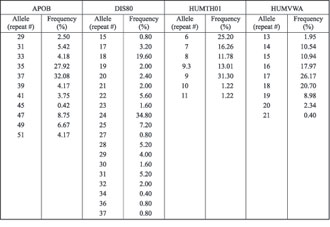
Table 2. Summary chart of statistical values for APOB, D1S80, HUMTH01 and HUMVWA in a Serbian population
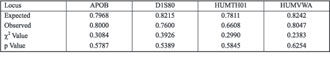
Table 3. Forensically relevant parameters for APOB, D1S80, HUMTH01 and HUMVWA in a Serbian population
|
|
|
|



 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (2), 2024 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (1), 2024 |
Number 26
Number 26 VOL. 26(2), 2023 All in one |
Number 26
VOL. 26(2), 2023 |
Number 26
VOL. 26, 2023 Supplement |
Number 26
VOL. 26(1), 2023 |
Number 25
VOL. 25(2), 2022 |
Number 25
VOL. 25 (1), 2022 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(2), 2021 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(1), 2021 |
Number 23
VOL. 23(2), 2020 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(2), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(1), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22, 2019 Supplement |
Number 21
VOL. 21(2), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21 (1), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21, 2018 Supplement |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (2), 2017 |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (1), 2017 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (2), 2016 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (1), 2016 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (2), 2015 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (1), 2015 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (2), 2014 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (1), 2014 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (2), 2013 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (1), 2013 |
Number 15
VOL. 15 (2), 2012 |
Number 15
VOL. 15, 2012 Supplement |
Number 15
Vol. 15 (1), 2012 |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (2), 2011 |
Number 14
The 9th Balkan Congress of Medical Genetics |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (1), 2011 |
Number 13
Vol. 13 (2), 2010 |
Number 13
Vol.13 (1), 2010 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (2), 2009 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (1), 2009 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (2),2008 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (1),2008 |
Number 10
Vol.10 (2), 2007 |
Number 10
10 (1),2007 |
Number 9
1&2, 2006 |
Number 9
3&4, 2006 |
Number 8
1&2, 2005 |
Number 8
3&4, 2004 |
Number 7
1&2, 2004 |
Number 6
3&4, 2003 |
Number 6
1&2, 2003 |
Number 5
3&4, 2002 |
Number 5
1&2, 2002 |
Number 4
Vol.3 (4), 2000 |
Number 4
Vol.2 (4), 1999 |
Number 4
Vol.1 (4), 1998 |
Number 4
3&4, 2001 |
Number 4
1&2, 2001 |
Number 3
Vol.3 (3), 2000 |
Number 3
Vol.2 (3), 1999 |
Number 3
Vol.1 (3), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.3(2), 2000 |
Number 2
Vol.1 (2), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.2 (2), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.3 (1), 2000 |
Number 1
Vol.2 (1), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.1 (1), 1998 |
|
|

