


CFTR MUTATIONS IN NORTHERN GREECE.
HIGH FREQUENCY OF MUTATION 621+1 (G->T)
Kalogeridis A1,2, Kouvatsi A1, Tsanakas I2
*Corresponding Author: Dr. Anastasia Kouvatsi, Department of Genetics, Development and Molecular Biology, School of Biology, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, 54006 Thessaloniki, Greece; Tel: +30310- 998361;
Fax: +30310-998374; E-mail: akouvats@bio.auth.gr
page: 11
|
|
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Samples and DNA analysis. DNA samples from 66 unrelated CF patients were studied. All these patients come from northern Greece (Thrace, Macedonia and Thessaly) and attend the Cystic Fibrosis Unit of the Hippokration General Hospital of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece. The geographical origin of the patients was established by assessing the birthplace of each of the patient's parents and grandparents. They were diagnosed by a positive sweat test and typical clinical findings. Genomic DNA was extracted from whole blood by the phenol-chloroform protocol. The DF508 mutation was detected by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) followed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE). Detection of mutations G551D, R553X, W1282X, N1303K, 621+1 (G®T), R334W, 1717–1 (G®A) and E822X [6-12] was carried out by using specific digestion of the PCR products with restriction enzymes (New England Biolabs, Inc., Boston, MA USA).
Dot-blot was used for the analysis of the G542X and R117H mutations by specific labeled radioactive probes [9,13].
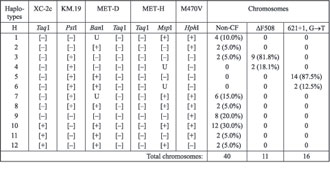
Haplotype analysis. The polymorphic extragenic markers Xv-2c/TaqI, KM19/PstI [13], MET-D/BanI-TaqI, MET-H/MspI-TaqI [15], upstream of the CFTR gene, and the intragenic marker M470V/HphI [9], were analyzed in the CF chromosomes of patients carrying the 621+1 (G®T) mutation. Furthermore, 40 non-CF chromosomes from unrelated individuals coming from northern Greece, were also analyzed for the same markers.
Table 1. Mutation and genotype frequencies identified in the CF patients from northern Greece (Thrace, Macedonia, and Thessaly.
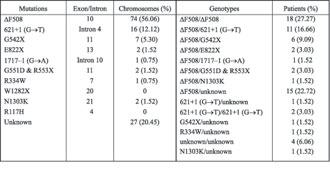
Table 2. Haplotype frequencies among the 621+1 (G®T), DF508 and non-CF chromosomes
|
|
|
|



 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (2), 2024 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (1), 2024 |
Number 26
Number 26 VOL. 26(2), 2023 All in one |
Number 26
VOL. 26(2), 2023 |
Number 26
VOL. 26, 2023 Supplement |
Number 26
VOL. 26(1), 2023 |
Number 25
VOL. 25(2), 2022 |
Number 25
VOL. 25 (1), 2022 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(2), 2021 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(1), 2021 |
Number 23
VOL. 23(2), 2020 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(2), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(1), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22, 2019 Supplement |
Number 21
VOL. 21(2), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21 (1), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21, 2018 Supplement |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (2), 2017 |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (1), 2017 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (2), 2016 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (1), 2016 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (2), 2015 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (1), 2015 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (2), 2014 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (1), 2014 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (2), 2013 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (1), 2013 |
Number 15
VOL. 15 (2), 2012 |
Number 15
VOL. 15, 2012 Supplement |
Number 15
Vol. 15 (1), 2012 |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (2), 2011 |
Number 14
The 9th Balkan Congress of Medical Genetics |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (1), 2011 |
Number 13
Vol. 13 (2), 2010 |
Number 13
Vol.13 (1), 2010 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (2), 2009 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (1), 2009 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (2),2008 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (1),2008 |
Number 10
Vol.10 (2), 2007 |
Number 10
10 (1),2007 |
Number 9
1&2, 2006 |
Number 9
3&4, 2006 |
Number 8
1&2, 2005 |
Number 8
3&4, 2004 |
Number 7
1&2, 2004 |
Number 6
3&4, 2003 |
Number 6
1&2, 2003 |
Number 5
3&4, 2002 |
Number 5
1&2, 2002 |
Number 4
Vol.3 (4), 2000 |
Number 4
Vol.2 (4), 1999 |
Number 4
Vol.1 (4), 1998 |
Number 4
3&4, 2001 |
Number 4
1&2, 2001 |
Number 3
Vol.3 (3), 2000 |
Number 3
Vol.2 (3), 1999 |
Number 3
Vol.1 (3), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.3(2), 2000 |
Number 2
Vol.1 (2), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.2 (2), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.3 (1), 2000 |
Number 1
Vol.2 (1), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.1 (1), 1998 |
|
|

