


CHROMOSOME TORSIONS IN CYTOGENETIC
PREPARATIONS OF BONE MARROW –
ARTIFACTS OR LEUKEMIA-SPECIFIC?
Glaser M1, Karst C1, Gross M1, Hasmik M2, Liehr T1,*
*Corresponding Author: Dr. Thomas Liehr, Institut für Humangenetik und Anthroplogie, Postfach, D-07740 Jena, Germany; Tel.: +49-3641-935533; Fax: +49-3641-935582; Email: i8lith@mti.uni-jena.de
page: 27
|
|
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients. Specimens of bone marrow, peripheral blood, skin fibroblasts, amniocytes and chorionic villi (CV) from 42 patients were studied. Bone marrow aspirates of eight patients with AML-M6, one each of persons suffering from AML-M1, AML-M4, AML-M5b and AML developing from myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), two with AML-M2, and four with different, non malignant bone marrow diseases (leukopenia of unclear origin, autoimmune disease, neutropenia, toxic bone marrow impairment or thrombocytopenia and anemia) were studied. Seven bone marrow aspirates from patients with rheumatoid arthritis were also included. All these specimens were cultivated in the presence of colcemid for 24 hours [6]. Seventy-two-hour cultures of six peripheral blood samples, three skin fibroblast, three amniocyte and one CV sample and four 24-hour cultures of different AML-cases and one 48-hour culture of AML case 38 (without permanent adding of colcemid) were used as controls (for further details see Table 1).
Cytogenetic and Molecular Cytogenetic. Banding analyses of chromosomes from peripheral blood was done according to standard procedures [7]. The search for cryptic chromosomal changes was done by mMCB [5]. To study the torsion anomaly in more detail, two-color fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) studies [8] using probes for 1p and 1q, 9p and 9q or 16p and 16q [9] were carried out (see Figs. 2 and 3).
Figure 1. Partial mMCB results by which the torsion phenomenon was detected in case 4: a) overlay of three-color channels (DAPI, TexasRed, FITC); b) pseudo color depiction of a chromosome 1 pair, that on the right shows the torsion; c) single chromosome 1 with a torsion depicted in pseudo colors, inverted DAPI, and the five-color channels: FITC, SpectrumOrange, TexasRed, Cyanine 5 and Diethylaminocoumarine.
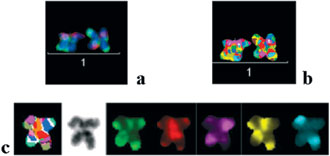
Figure 2. Pairs of chromosomes 1, 9 and 16. For the examples presented for chromosomes 1 and 16, those on the right show the chromosome torsion. In the example for chromosome 9, both chromosomes have a torsion.
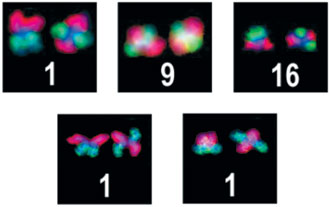
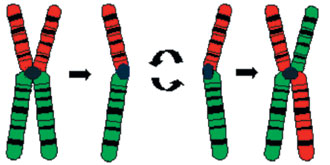
Figure 3. Schematic drawing of the torsion anomaly for chromosome 1.
|
|
|
|



 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (2), 2024 |
Number 27
VOL. 27 (1), 2024 |
Number 26
Number 26 VOL. 26(2), 2023 All in one |
Number 26
VOL. 26(2), 2023 |
Number 26
VOL. 26, 2023 Supplement |
Number 26
VOL. 26(1), 2023 |
Number 25
VOL. 25(2), 2022 |
Number 25
VOL. 25 (1), 2022 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(2), 2021 |
Number 24
VOL. 24(1), 2021 |
Number 23
VOL. 23(2), 2020 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(2), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22(1), 2019 |
Number 22
VOL. 22, 2019 Supplement |
Number 21
VOL. 21(2), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21 (1), 2018 |
Number 21
VOL. 21, 2018 Supplement |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (2), 2017 |
Number 20
VOL. 20 (1), 2017 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (2), 2016 |
Number 19
VOL. 19 (1), 2016 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (2), 2015 |
Number 18
VOL. 18 (1), 2015 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (2), 2014 |
Number 17
VOL. 17 (1), 2014 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (2), 2013 |
Number 16
VOL. 16 (1), 2013 |
Number 15
VOL. 15 (2), 2012 |
Number 15
VOL. 15, 2012 Supplement |
Number 15
Vol. 15 (1), 2012 |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (2), 2011 |
Number 14
The 9th Balkan Congress of Medical Genetics |
Number 14
14 - Vol. 14 (1), 2011 |
Number 13
Vol. 13 (2), 2010 |
Number 13
Vol.13 (1), 2010 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (2), 2009 |
Number 12
Vol.12 (1), 2009 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (2),2008 |
Number 11
Vol.11 (1),2008 |
Number 10
Vol.10 (2), 2007 |
Number 10
10 (1),2007 |
Number 9
1&2, 2006 |
Number 9
3&4, 2006 |
Number 8
1&2, 2005 |
Number 8
3&4, 2004 |
Number 7
1&2, 2004 |
Number 6
3&4, 2003 |
Number 6
1&2, 2003 |
Number 5
3&4, 2002 |
Number 5
1&2, 2002 |
Number 4
Vol.3 (4), 2000 |
Number 4
Vol.2 (4), 1999 |
Number 4
Vol.1 (4), 1998 |
Number 4
3&4, 2001 |
Number 4
1&2, 2001 |
Number 3
Vol.3 (3), 2000 |
Number 3
Vol.2 (3), 1999 |
Number 3
Vol.1 (3), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.3(2), 2000 |
Number 2
Vol.1 (2), 1998 |
Number 2
Vol.2 (2), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.3 (1), 2000 |
Number 1
Vol.2 (1), 1999 |
Number 1
Vol.1 (1), 1998 |
|
|

